|
个人信息:Personal Information
副教授 硕士生导师
教师英文名称:Xiaoxi Li
教师拼音名称:lixiaoxi
所在单位:医学院
职称:副教授
毕业院校:分子细胞科学卓越创新中心
硕士生导师
学科:临床检验诊断学
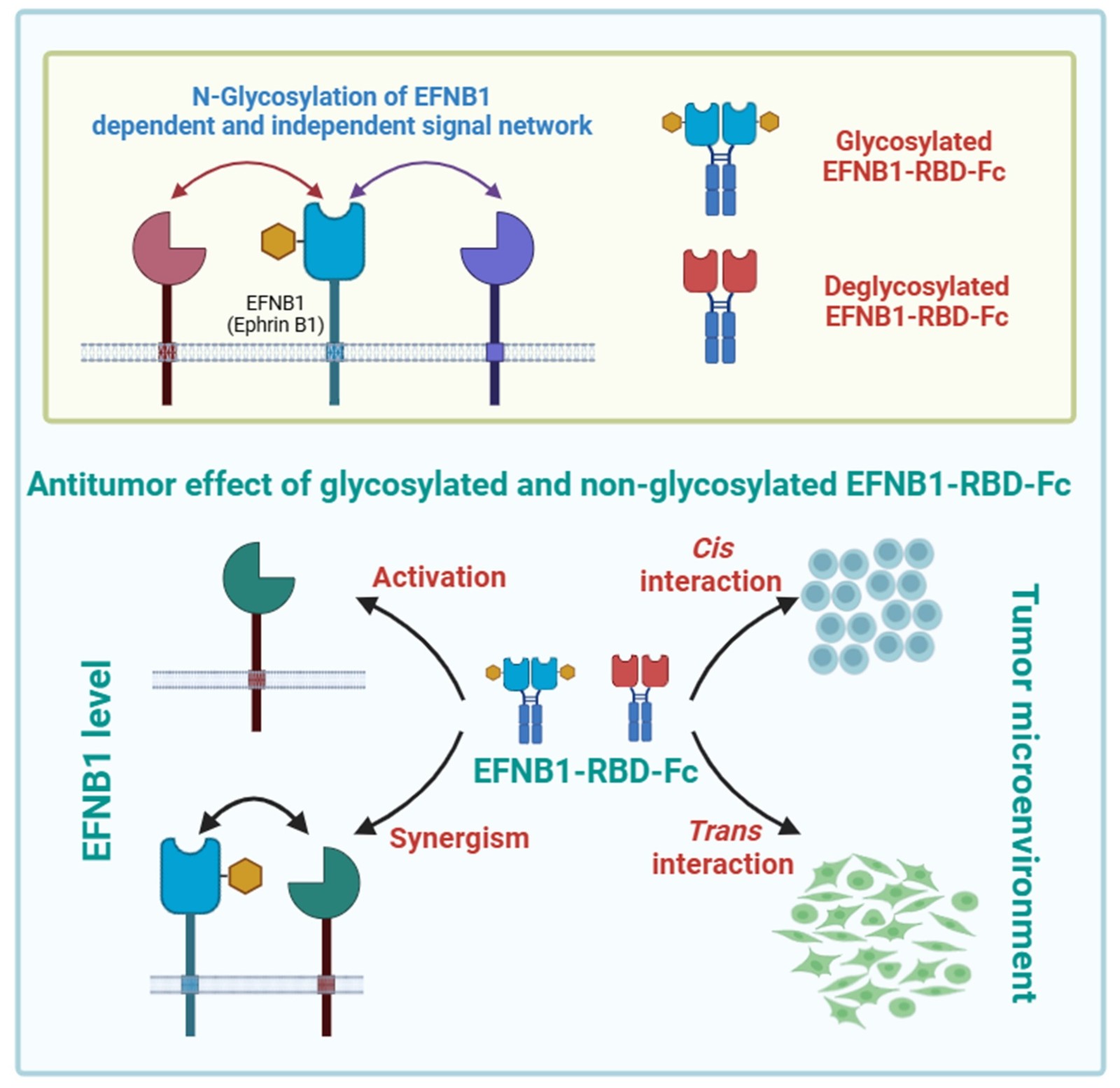
(1) Li Xiaoxi; Jiang Yong*; Deng Minyao*; Zhang Chenxiao; Tang Hua; N-glycosylation of ephrin B1 modulates its function and confers therapeutic potential in B-cell lymphoma, Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2025
Abstract: Given the pivotal role of the Eph-Ephrin signaling pathway in tumor progression, agonists or antagonists targeting Eph/Ephrin have emerged as promising anticancer strategies. However, the implications of glycosylation modifications within Eph/Ephrin and their targeted protein therapeutics remain elusive. Here, we identify that N-glycosylation within the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of ephrin B1 (EFNB1) is indispensable for its functional repertoire. Notably, compared to wild-type EFNB1, the glycosylation-deficient N139D mutant drastically diminishes the sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapeutic agents, suggesting the existence of both glycosylation-dependent and independent effects mediated by EFNB1. Transcriptomic analysis highlights immune response and oxidative phosphorylation as the primary signaling pathways modulated by glycosylation modifications. In coculture systems, the EFNB1-RBD-Fc recombinant protein, while inhibiting B-lymphoma cells, also exerts differential impacts on stromal cells depending on their glycosylation status. Furthermore, the efficacy of both glycosylated and non-glycosylated EFNB1-RBD-Fc is influenced by the endogenous EFNB1 levels within tumor cells. Taking together, this study demonstrates the complexity and multifaceted roles of glycosylation in modulating EFNB1 function. These findings underscore the need for a nuanced understanding of glycosylation patterns in Eph/Ephrin-targeted therapies to optimize their therapeutic potential.